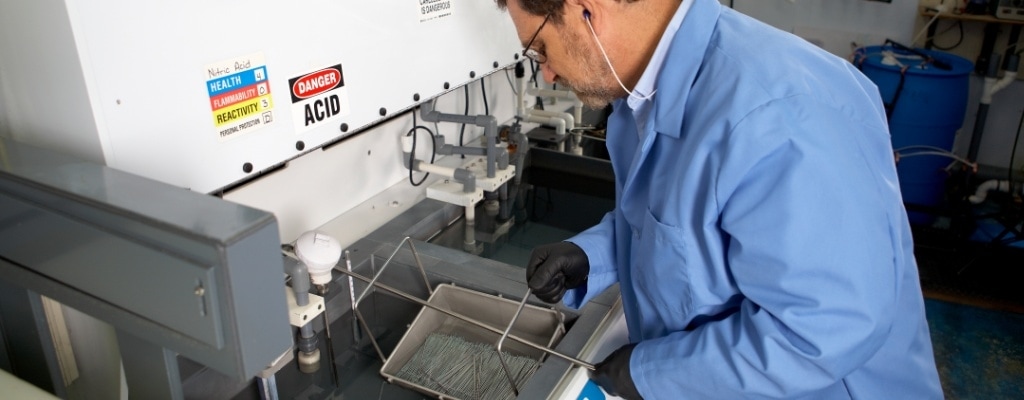

Cleaning
Cleaning and passivation are critical steps in medical device component manufacturing to remove contaminants and improve corrosion resistance from metal components such as hypotubes. TE performs state-of-the-art fully automated cleaning and passivation processes with precision and accuracy, meeting industry standards such as ASTM A380 and ASTM A967.
Clean, high-quality, low-defect parts directly improve the process efficiency of medical device assembly. TE stays ahead of cleaning problems found in batch processing by using automated systems to clean, rinse, flush solvents, and purge. With the support of experienced chemical engineers, TE has built a state-of-the-art cleaning and passivation systems for its metal components. These systems have been built to account for environmental considerations and the health and safety of personnel working in the area. There are dedicated cleaning systems to support specific components for different medical devices applications.
We feature five standard cleaning processes, plus custom solutions to meet your needs.
Vapor Degreasing
Vapor degreasing is a cost-efficient, noncombustible, environmentally-friendly method of removing oils and greases from metal surfaces. TE offers a fully automated process that employs a programmable PLC control with a robotic arm to expose workpieces to hot vapors from n-propyl bromide (nPB) based solvent. Surface soils on the part dissolve from the solvent vapor and are shed via gravity. The process uses less energy and creates less waste than other cleaning methods.
Ultrasonic
Hot alkaline aqueous ultrasonic cleaning is a staple of the metal working industry to remove contaminants and restore surface finishes. We use twin cascading deionized rinse tanks with PLC-controlled actuation of the ultrasonic cycle. We monitor the conductivity of the water to produce final rinse values of less than 50µS for most applications.
Pickling / Acid etching
Pickling uses chemicals to remove the oxides and corrosion that occur on stainless steel surfaces during manufacturing processes such as soldering, welding, annealing, and electrical discharge machining (EDM). The pickling process at TE treats the surface of stainless steel to remove contaminants and improve corrosion resistance.
Though pickling renders stainless steel and other metals as passive, TE can further treat parts with citric or nitric baths or electropolishing. Pickling is also an option to achieve a consistent surface finish, though coloration may change over time on materials that oxidize with age such as copper and solders.

Passivation
Passivation treats the surface of stainless steel with a thin, dense, uniform film to remove contaminants and improve corrosion resistance. TE offers methods of passivating per ASTM A967. Our in-house passivation testing follows ASTM A967 Practice D–Copper Sulfate Test. We can also accommodate additional testing requirements through partnership with local analytical laboratories.

Electropolishing
Electropolishing uses electro chemicals to remove surface defects for a clean, uniform, bright-looking appearance. TE’s electropolishing process can achieve a two-fold improvement in surface finishes within close dimensional tolerances. We use an electrically controlled tank to submerge parts into a specially formulated acid bath where a DC current is applied. Parts that are electropolished are shinier and more passive than those produced through a chemical passivation process.
TE builds custom electropolish racks for consistent component processing with optimized rack mark placement. In addition to exterior part surfaces, TE offers interior surface electropolishing within limits determined by the engineering staff.
