The minimally invasive medical device industry is a dynamic industry, evolving to deliver smaller and more complex devices to treat all kinds of medical issues. Precision manufacturing of laser processed components tailored for these dynamic needs is becoming more critical. In this Device Talks Tuesdays webinar, the TE experts discuss how you can harness cutting-edge laser technology, both cutting and welding, to complete your new delivery and access device or enhance your existing device.
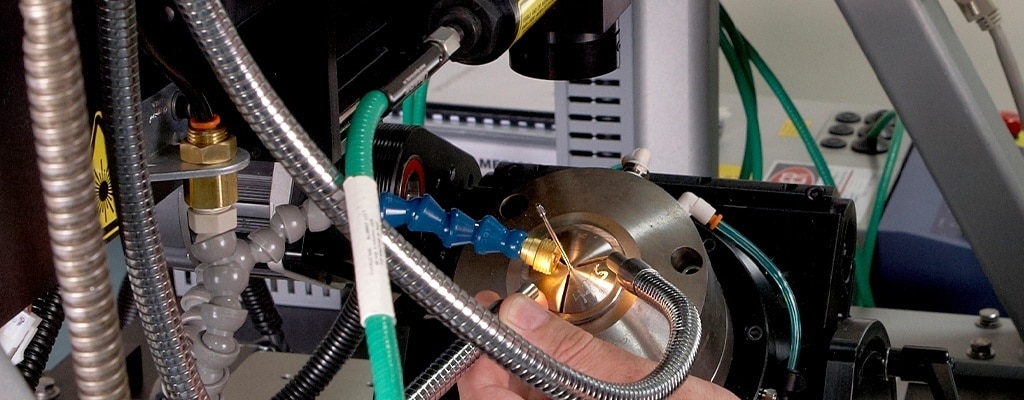

Medical Device Laser Cutting
Lasers provide fast, repeatable, distortion-free cuts on extremely precise and/or geometrically intricate materials. Because it is a non-contact, clean process, laser cutting is suitable for thin-wall, fragile medical device components.
TE uses CNC-controlled laser machines on device micro-components to create radically thin, precise cuts with optimized end-face surface finish and edge quality. These lasers can repeatedly cut metal in thicknesses from 0.125” (0,3175 cm) down to 0.001” (0,00254 cm), and can cut slots as thin as 0.0008” (0,002032 cm). Laser-cutting medical devices mitigates the threat of contaminants since no blades or cutting tools touch component surfaces. For reliable, repeatable cuts on intricate designs, TE is your high-performance provider of rapid and cost-effective medical laser cutting services at scale.
Applications
Many medical devices require intricate, geometrically-complex micro-components produced within strict tolerances. TE offers fast, precise laser-cutting solutions for metal, plastic, and polymer materials at a lower cost than traditional machining or EDM methods. We laser cut standard or pattern tubing, wires, and solids that are used in:
- Surgical instruments
- Laparoscopic instruments
- Catheter subassemblies
- Tubular devices
- Drug delivery ports
- And many other medical device parts
Materials & Specifications
TE supports a diverse range of composites and metals including stainless steel, nitinol, nickel, cobalt chromium, and MP35N. High-performance specifications on plastic and metal materials include:
- Tolerances within 0.0005” (0,00127 cm) or less
- Kerf width as small as 0.0007” (0,001778 cm)
- Process small wall thicknesses as thin as 0.002” (0,00508 cm) up to 0.030” (0,0762 cm)
- Process diameter tubing (i.e. 0.012” x 0.009” (0,03048 cm x 0,02286 cm))
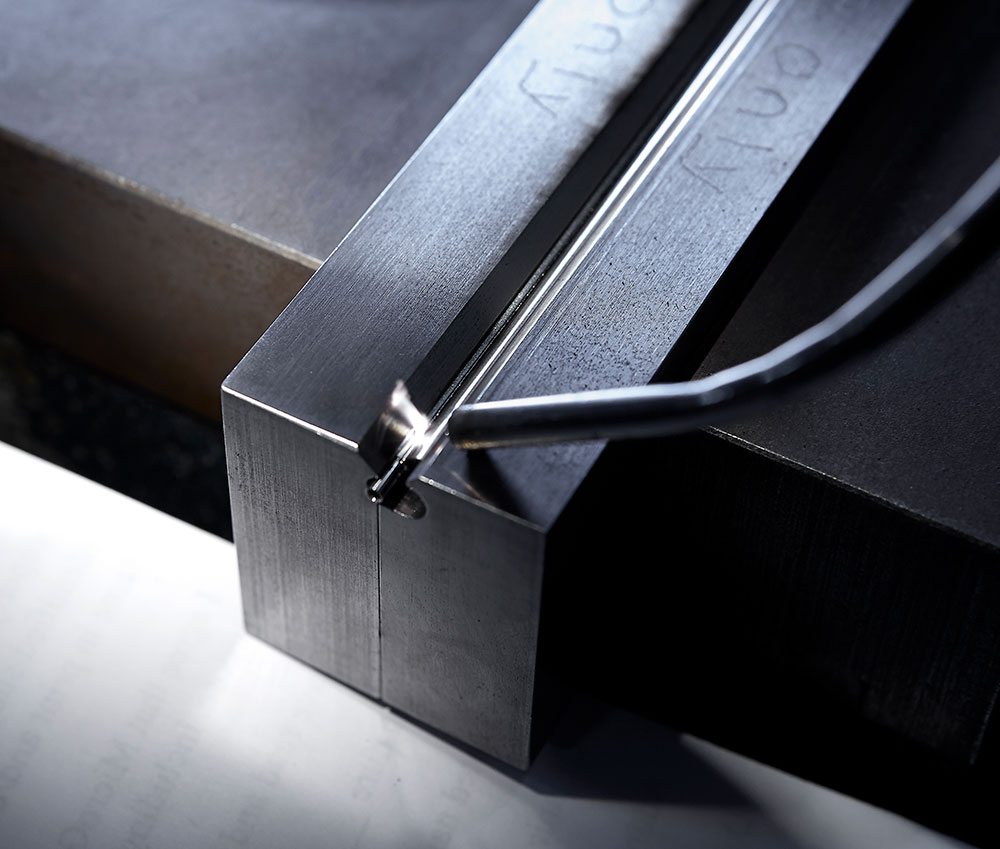


Manufacturing Locations
Technical Resources
The move toward smaller medical devices has established laser cutting & welding as critical methods of medical device manufacturing. These methods are complicated but essential processes for adding functionality such as improved steering, reach or flexibility when working with materials such as metals and polymers. TE is leading a discussion about its laser processing capabilities in cutting and welding complex designs of metal components, from prototyping through to automated high-volume production.
 e
e
 e
e
 e
e
 e
e
 e
e

 e
e
 e
e
 e
e
 e
e
 e
e
