The minimally invasive medical device industry is a dynamic industry, evolving to deliver smaller and more complex devices to treat all kinds of medical issues. Precision manufacturing of laser processed components tailored for these dynamic needs is becoming more critical. In this Device Talks Tuesdays webinar, the TE experts discuss how you can harness cutting-edge laser technology, both cutting and welding, to complete your new delivery and access device or enhance your existing device.
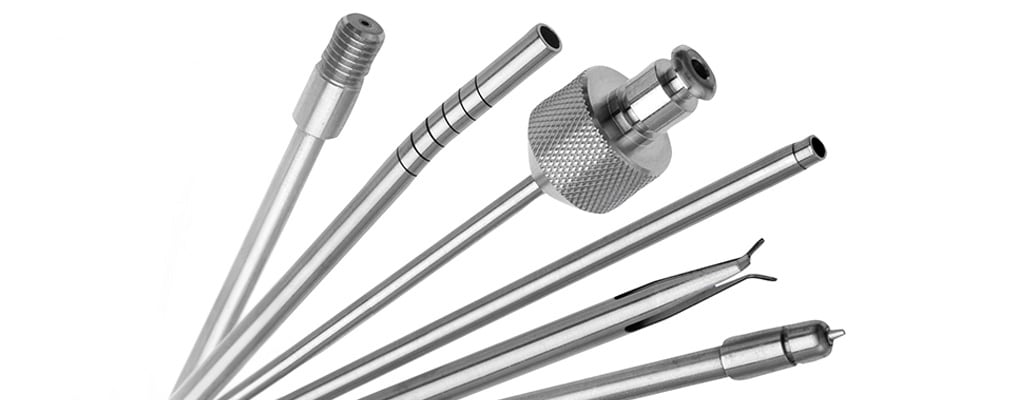

Medical Device Laser Welding
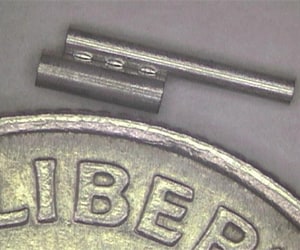
Laser welding is the process of joining similar or dissimilar materials with exceptional strength and durability. Because it can create narrow, deep welds with repeatable precision, laser welding is suitable for fusing delicate materials.
TE’s medical laser welding services features a high degree of control to deliver precision welds with minimal heat impact on surrounding material zones. With superior joint strength with a clean cosmetic finish, laser welded components are easily assembled into a variety of small-diameter medical devices such as catheter shafts, guidewires, hypodermic tubing, pacemaker cases, diaphragms, bellows, and more. For customers seeking an extremely clean welding process that leaves minimal post-processing steps, TE delivers fast, precise laser welding services that power microscale medical devices.
Applications
Microscale medical devices are built on components fused into clean, defect-free surfaces. TE uses tight process controls and practices during the laser welding process to minimize biocompatibility issues for medical applications. Our lasers can be positioned into tight geometry for contact-free, fast, repeatable welds with minimal heat-affected zones around joint sites. We use no fillers when welding similar and dissimilar materials that are used for:
- Proximal shaft assemblies (hypotube to wire weld)
- Guidewires (coil to coil and coil to ground wire)
- Torque cables
- Catheter tips
- Tube assemblies
- Wire ball forming
- And many other medical components
Materials & Specifications
Our laser welding process supports hermetic environments, helically-oriented coils, lap and butt configurations, and more. Materials include:
- Stainless steels: 304, 316, 17-4, 420, 302, 303 and others
- Nitinol, platinum and platinum alloys, and titanium
- ELGILOY™ alloy, nichrome, INVAR™ alloy, MP35N™ and L605
TE uses high-precision lasers for weld walls as thin as 0.002” (0,00508 cm) with laser spot sizes as small as 0.004” (0.0102 cm). TE supports high volume welding of medical components, welding over ¼ of a million parts every week across our network of sites, including multiple automated lines welding 80’000 units each per week.

Manufacturing Locations
Technical Resources
The move toward smaller medical devices has established laser cutting & welding as critical methods of medical device manufacturing. These methods are complicated but essential processes for adding functionality such as improved steering, reach or flexibility when working with materials such as metals and polymers. TE is leading a discussion about its laser processing capabilities in cutting and welding complex designs of metal components, from prototyping through to automated high-volume production.
 e
e
 e
e
 e
e
 e
e
 e
e
 e
e

 e
e
 e
e
 e
e
 e
e
 e
e
