Sealing, Protection & EMC Design Considerations in eMobility Applications
Download WhitepaperAs the world continues to make the shift to e-mobility, there is an increasing demand for charging infrastructure, and it is becoming part of our daily life. Charging your car at home or at work requires standard Alternative Current (AC) home charging units and workplace charging units. AC charging units can be economically effective and can be installed with great flexibility. Direct Current (DC) charging stations can have a very quick charging rate as little as 30 minutes. The rapid, global growth of EVs requires the development of a charging infrastructure that is faster, safer, smaller and more flexible, which creates design challenges for engineers around the world.
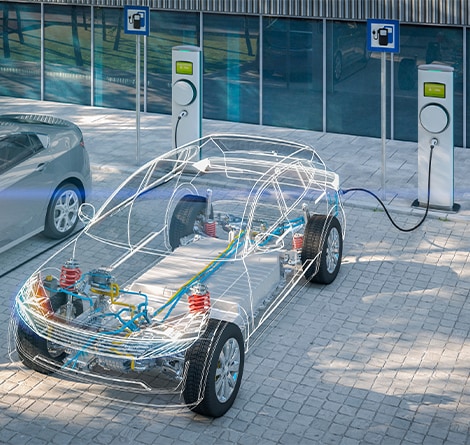
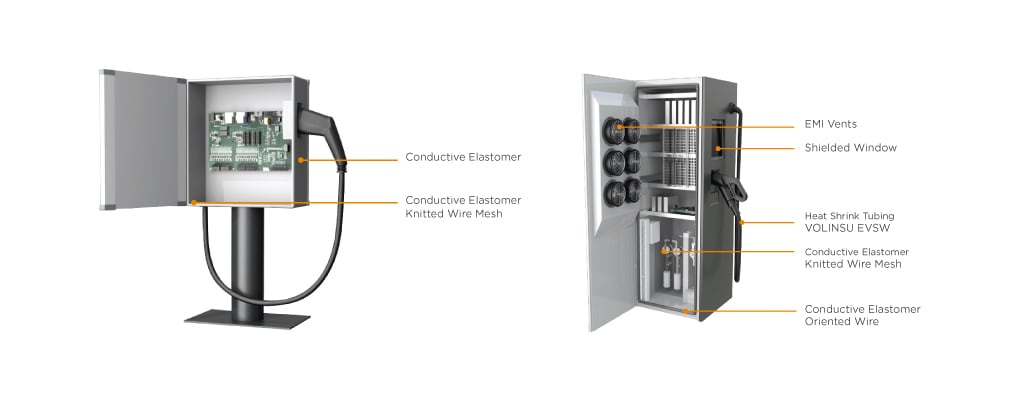
Electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) are intricate systems comprising a variety of electronic components. These components function in unison to provide safe and efficient charging of electric vehicle batteries. Much like other advanced, high-power electronic devices, these EVSE stations can encounter issues related to thermal management and EMI shielding that need to be addressed for proper and efficient operation.
Electric charging stations (ECS) represent a source of EMI due to the presence of AC and DC magnetic fields. The onboard electronics of the ECS require shielding from EMI as well. Additionally, the electric vehicle is susceptible to external sources of EMI ranging from common household items like garage door openers and cell phones to less frequently encountered sources like solar storms and high voltage power lines.
EV Charging Solutions